Info
© 2026 Feels Co.
 Summary & key points
Summary & key points
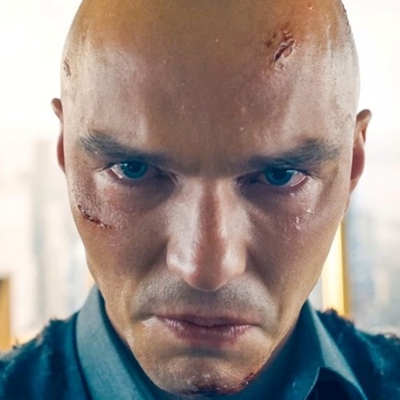
In Superman (2025), Lex Luthor blew a gasket after he learned that Superman escaped his prison. So much so, in fact, that Lex screamed out loud and began to throw things on the floor and at his soon-to-be ex-girlfriend.
 Summary & key points
Summary & key points
In the hit sequel movie The Matrix Reloaded (2003), Neo goes to meet the Oracle, who can allegedly see the future. Without even looking, she tells Neo what is going to happen next on several occasions. This ability to engage in 'mental time travel' with events that have not happened yet highlights the Inference attribute to a degree that no real person can emulate.
 Summary & key points
Summary & key points
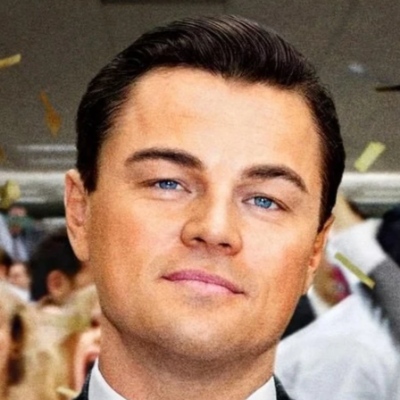
In the hit movie The Wolf of Wall Street (2013), future successful financer Jordan Belfort is starting out on his first day of work as a broker on Wall Street. His boss takes him out to lunch and proceeds to take several drugs and order lots of alcoholic beverages in the work day. When Jordan questions his boss about this, he soon discovers that the culture of Wall Street includes such behavior, and many others. This alters Jordan's perspective on how things really work on Wall Street. Jordan's initial inability to adapt his speech and behavior with respect to Formality, Emotion, and other attributes highlight a well-below average score of Apperception.
 Summary & key points
Summary & key points
In rock band Blondie's 1978 hit single called Heart of Glass, the lyrics tell us about the potential disappointment of romance. The entire song features a single example of colorful language: "... soon turned out to be a pain in the a**." This limited, tame use of colorful language exemplifies the Formality attribute.
 Summary & key points
Summary & key points
In the hit movie The Fast and the Furious: Tokyo Drift (2006), outlaw teenager Sean Boswell finds himself in Japan after getting kicked out of America by the law and his own mother. After befriending a car enthusiast at school, he's in an underground car enthusiast meetup focused on a style of racing called drifting. As he's walking around, Sean spots a girl from his class and begins flirting with her while discussing technical aspects of car engines. Soon, though, the girl's boyfriend notices and walks over to join the conversation. Sean doesn't realize that the man is part of the crime family known as the Yakuza, and continues taunting him. Despite warnings from two people, Sean decides to race DK ("Drift King") after being allowed to borrow another character's car. Sean bombs the race, wrecks the car, and eats his words because of his inexperience with the drift style of racing. Sean's inability to self-monitor his aggression and impulses in a dangerous, novel setting demonstrates a total lack of the Apperception attribute.